Hello,welcome to our blog. Hope you enjoy reading :)
|
Sheng Siong Supermarket is the place that we decided to go.Our task is to find products that are categorised under homologous series.Examples of homologous series are Alkene,Alkane,Alcohol and Carboxylic acid.The main purpose of completing this task is to learn more about organic chemistry. Here is a brief explanation of homologous series: Homologous series is a series of organic compounds with a similar general formula, possessing similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group, and shows a gradation in physical properties as a result of increase in molecular size and mass.For example, ethane has a higher boiling point than methane since it has more Van der Waals forces(intermolecular forces) with neighbouring molecules. This is due to the increase in the number of atoms making up the molecule. Organic compounds in the same homologous series vary by a CH2.
Alkene  Item: Item: Palmolive
Uses: It is a shower gel for massage
Substances available: butylene, ethylene
What is butylene? Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula C4H8. It is a colourless gas that is present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for viable extraction. Structure of Butene What is ethylene?
Ethylene, also known as ethene, is an alkene with the formula C2H4. It contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is called an unsaturated hydrocarbon. And it is a colourless gas. Structure of ethene
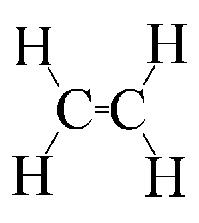

Item: EverSoft Shower Foam Uses: It is a shower foam for hair Substances available: propylene, styrene What is propylene? Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound having the chemical formula C3H6. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons, and it is also second in natural abundance. Structure of Propene What is styrene? Styrene, also known as phenylethene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. Under normal conditions, this aromatic hydrocarbon is an oily liquid. It evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations confer a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene, an important synthetic material. Structure of Styrene
Alkane
Item: Loreal Sculpting Mousse Uses: It is used to style the hair Substance available: butane, propane, isobutane What is butane? Butane, also called n-butane, is the unbranched alkane with four carbon atoms, CH3CH2CH2CH3. The chemical formula is C4H10. Structure of Butane What is isobutane? What is isobutane?Isobutane, also known as methylpropane or 2-methylpropane, is an alkane, isomeric with butane.
Structure of Isobutane
What is propane? Propane is an alkane with the formula C3H8. It is a three-carbon alkane, normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. Structure of Propane
Alcohol 
Item: Gold Cow
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: dexpanthenol
What is dexpanthenol? Dexpanthenol,also known as panthenol is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid. The molecular formula is C9H19NO4.
Structure of panthenol
Item: Loreal Sculpting Mousse
Uses: It is used to style the hair
Substance available: phenoxyethanol
What is phenoxyethanol? Phenoxyethanol is an organic chemical compound, a glycol ether often used in dermatological products such as skin creams and sunscreen. It is a colorless oily liquid. The molecular formula is C8H10O2.
Structure of phenoxyethanol
Carboxylic Acid
Item: Garlic Chilli
Uses: It is used for ingredients of food
Substance available: acetic acid
What is acetic acid? Acetic acid, CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid, is an organic acid which gives vinegar its sour taste and pungent smell.
Structure of Ethanoic acid
Item: Wang Wang Milk
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: docosahexaenoic acid
What is docosahexaenoic acid?
Docosahexaenoic acid, commonly known as DHA, is a carboxylic acid with a 22-carbon chain and six cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end. Structure of Docosahexaenoic acid
Item: Horlick
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: pantothenic acid
What is pantothenic acid?
Pantothenic acid, also called vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin required to sustain life. The molecular formula is C9H17NO5.
Item: Promil Gold
Uses: For babies to drink
Substance available: arachiodonic acid
What is arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and four cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the omega end. The molecular formula is C20H32O2.
Structure of Arachidonic acid
|
S.A.R.S

Siti. Aston. Ruijian. Sharon
Sheng Siong Supermarket is the place that we decided to go.Our task is to find products that are categorised under homologous series.Examples of homologous series are Alkene,Alkane,Alcohol and Carboxylic acid.The main purpose of completing this task is to learn more about organic chemistry. Here is a brief explanation of homologous series: Homologous series is a series of organic compounds with a similar general formula, possessing similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group, and shows a gradation in physical properties as a result of increase in molecular size and mass.For example, ethane has a higher boiling point than methane since it has more Van der Waals forces(intermolecular forces) with neighbouring molecules. This is due to the increase in the number of atoms making up the molecule. Organic compounds in the same homologous series vary by a CH2.
Alkene  Item: Item: Palmolive
Uses: It is a shower gel for massage
Substances available: butylene, ethylene
What is butylene? Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula C4H8. It is a colourless gas that is present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for viable extraction. Structure of Butene What is ethylene?
Ethylene, also known as ethene, is an alkene with the formula C2H4. It contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is called an unsaturated hydrocarbon. And it is a colourless gas. Structure of ethene


Item: EverSoft Shower Foam Uses: It is a shower foam for hair Substances available: propylene, styrene What is propylene? Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound having the chemical formula C3H6. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons, and it is also second in natural abundance. Structure of Propene What is styrene? Styrene, also known as phenylethene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. Under normal conditions, this aromatic hydrocarbon is an oily liquid. It evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations confer a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene, an important synthetic material. Structure of Styrene
Alkane
Item: Loreal Sculpting Mousse Uses: It is used to style the hair Substance available: butane, propane, isobutane What is butane? Butane, also called n-butane, is the unbranched alkane with four carbon atoms, CH3CH2CH2CH3. The chemical formula is C4H10. Structure of Butane What is isobutane? What is isobutane?Isobutane, also known as methylpropane or 2-methylpropane, is an alkane, isomeric with butane.
Structure of Isobutane
What is propane? Propane is an alkane with the formula C3H8. It is a three-carbon alkane, normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. Structure of Propane
Alcohol 
Item: Gold Cow
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: dexpanthenol
What is dexpanthenol? Dexpanthenol,also known as panthenol is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid. The molecular formula is C9H19NO4.
Structure of panthenol
Item: Loreal Sculpting Mousse
Uses: It is used to style the hair
Substance available: phenoxyethanol
What is phenoxyethanol? Phenoxyethanol is an organic chemical compound, a glycol ether often used in dermatological products such as skin creams and sunscreen. It is a colorless oily liquid. The molecular formula is C8H10O2.
Structure of phenoxyethanol
Carboxylic Acid
Item: Garlic Chilli
Uses: It is used for ingredients of food
Substance available: acetic acid
What is acetic acid? Acetic acid, CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid, is an organic acid which gives vinegar its sour taste and pungent smell.
Structure of Ethanoic acid
Item: Wang Wang Milk
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: docosahexaenoic acid
What is docosahexaenoic acid?
Docosahexaenoic acid, commonly known as DHA, is a carboxylic acid with a 22-carbon chain and six cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end. Structure of Docosahexaenoic acid
Item: Horlick
Uses: For drinking
Substance available: pantothenic acid
What is pantothenic acid?
Pantothenic acid, also called vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin required to sustain life. The molecular formula is C9H17NO5.
Item: Promil Gold
Uses: For babies to drink
Substance available: arachiodonic acid
What is arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and four cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the omega end. The molecular formula is C20H32O2.
Structure of Arachidonic acid
|





















